No products in the cart.
2023 Guide to Ophthalmic Imaging: A Comprehensive Overview Leave a comment
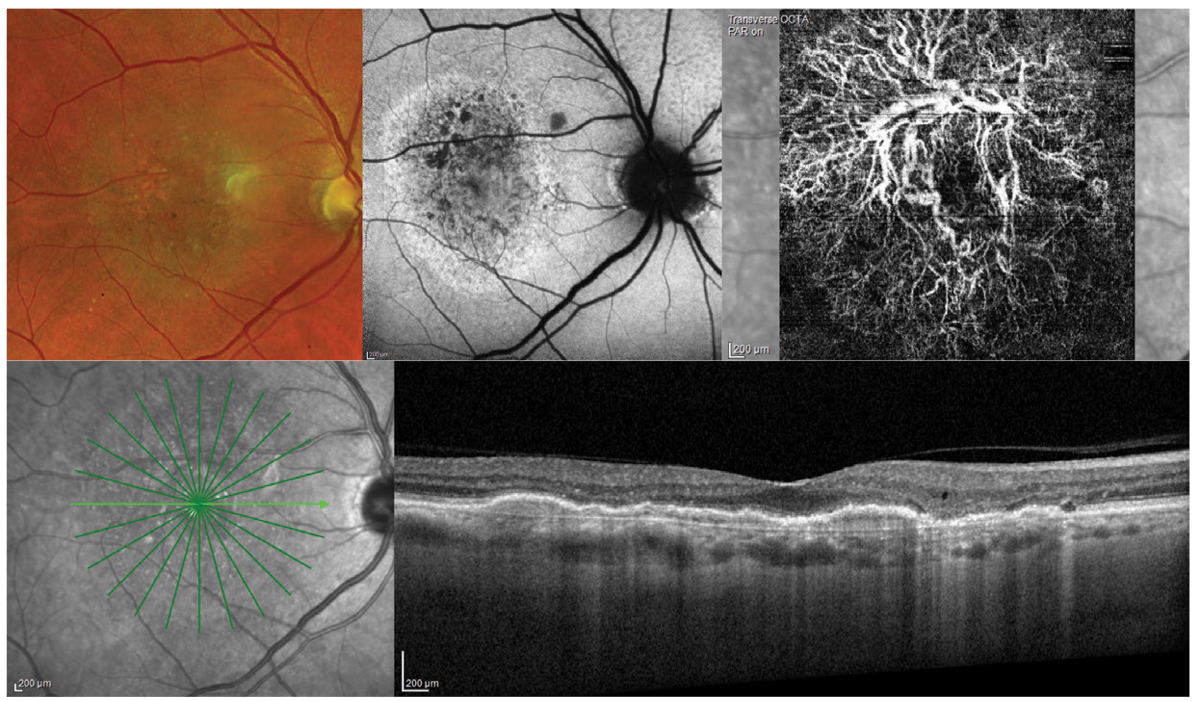
Ophthalmic imaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of various eye conditions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ophthalmic imaging, covering everything from its definition and applications to the best resources available for further learning. So, let’s dive into this fascinating field!
Visit the store to download the Ophthalmic Imaging Books for only 1/10 of the original price : https://ophthalmologyebooks.store
Who Uses Ophthalmic Imaging and Why?
Ophthalmic imaging is primarily used by ophthalmologists, optometrists, and other eye care professionals to evaluate and document ocular health. It enables them to visualize intricate structures within the eye, such as the retina, optic nerve, and cornea, aiding in the detection and management of diseases like glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy.
What Is Ophthalmic Imaging?
Ophthalmic imaging refers to the use of specialized techniques and equipment to capture high-resolution images of the eye. These images provide valuable insights into the anatomical and physiological characteristics of ocular structures, allowing healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and formulate effective treatment plans.
When Should Ophthalmic Imaging Be Utilized?
Ophthalmic imaging should be utilized in various clinical scenarios, including:
- Routine Eye Examinations: Ophthalmic imaging can help detect early signs of eye diseases before symptoms become apparent, enabling timely intervention.
- Disease Monitoring: Imaging techniques allow for the precise tracking of disease progression, guiding treatment adjustments as necessary.
- Surgical Planning: Ophthalmologists rely on preoperative imaging to assess ocular structures and plan surgical procedures with enhanced precision.
- Patient Education: Visual representations obtained through imaging facilitate patient understanding of their condition and the recommended interventions.
How to Conduct Ophthalmic Imaging?
Ophthalmic imaging requires specialized equipment and expertise. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how the process is typically conducted:
- Prepare the Patient: Ensure the patient is comfortable and understands the procedure.
- Positioning and Alignment: Properly position the patient and adjust the imaging device to align with the target area of the eye.
- Capture the Image: Depending on the technique employed, capture images using instruments such as fundus cameras, optical coherence tomography (OCT) machines, or ultrasound devices.
- Documentation: Store and label the captured images for future reference and comparison.
- Analysis and Interpretation: Skilled professionals analyze the images, identifying any abnormalities and determining the appropriate course of action.
Pros and Cons of Ophthalmic Imaging
Like any medical procedure, ophthalmic imaging has its pros and cons:
Pros:
- Early Detection: Enables early identification of eye diseases, leading to prompt treatment initiation.
- Accuracy: Provides detailed and precise visual information about ocular structures.
- Non-invasive: Most imaging techniques are non-invasive, ensuring patient comfort and safety.
- Progress Monitoring: Allows for monitoring disease progression and response to treatment over time.
Cons:
- Costs: Some advanced imaging techniques can be expensive.
- Training and Expertise: Conducting and interpreting imaging requires specialized training and expertise.
- Limitations: Certain eye conditions, such as cataracts or severe corneal opacities, may hinder image quality.
- Accessibility: High-quality imaging equipment may not be readily available in all healthcare settings.
Alternatives to Ophthalmic Imaging
While ophthalmic imaging remains the gold standard for evaluating ocular health, alternative approaches may be considered in specific situations. These alternatives include:
- Clinical Examination: Comprehensive eye examinations involving direct observation, visual acuity tests, and other diagnostic maneuvers.
- Functional Tests: Assessments that evaluate specific aspects of visual function, such as perimetry for measuring visual field defects.
- Biopsy or Histopathology: In cases where a tissue sample is required for diagnosis, a biopsy followed by histopathological examination may be necessary.
Comparing Ophthalmic Imaging Techniques
Several ophthalmic imaging techniques are available today. Here’s a quick comparison of some commonly used ones:
- Fundus Photography: Captures detailed images of the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Produces cross-sectional images of retinal layers, aiding in the diagnosis of macular diseases and glaucoma.
- Fluorescein Angiography (FA): Evaluates retinal blood flow and identifies abnormalities using a contrast agent.
- Ultrasound Biomicroscopy (UBM): Offers high-resolution images of the anterior segment, essential for assessing conditions like angle-closure glaucoma.
Tips for Effective Ophthalmic Imaging
To ensure optimal results during ophthalmic imaging, consider the following tips:
- Patient Preparation: Educate patients about the procedure to alleviate anxiety and obtain their cooperation.
- Image Quality: Pay attention to factors such as focus, lighting, and patient fixation to capture clear and accurate images.
- Documentation: Maintain adetailed record of each imaging session, including patient information, image acquisition parameters, and any relevant clinical findings.
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate the imaging equipment to ensure accurate measurements and consistent image quality.
- Continued Education: Stay updated with advancements in ophthalmic imaging technology and techniques through conferences, workshops, and reputable resources like ophthalmic imaging books.
The Best Ophthalmic Imaging Books for Further Learning
To expand your knowledge in ophthalmic imaging, here are some highly recommended books:
- Angio OCT in Everyday Ophthalmic Practice by Bruno Lumbroso (Author), David Huang (Author), Marco Rispoli (Author)
- Ophthalmic Imaging: Posterior Segment Imaging, Anterior Eye Photography, and Slit Lamp Biomicrography (Applications in Scientific Photography) by Christye Sisson (Author), Michael Peres (Series Editor)
- Principles of Ocular Imaging by Daniel Gologorsky MD MBA (Author), Richard B Rosen MD (Author)
These comprehensive resources provide in-depth explanations, case studies, and high-quality images to enhance your understanding of ophthalmic imaging techniques and their applications.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Q: Is ophthalmic imaging painful? A: No, ophthalmic imaging is a non-invasive procedure and does not cause pain or discomfort.
- Q: Can ophthalmic imaging be performed on children? A: Yes, ophthalmic imaging can be safely conducted on children of all ages, but it may require additional measures to ensure cooperation.
- Q: Are there any risks associated with ophthalmic imaging? A: Generally, ophthalmic imaging is considered safe. However, rare cases of allergic reactions to contrast agents or temporary vision disturbances may occur.
- Q: How long does an ophthalmic imaging session typically take? A: The duration varies depending on the specific imaging technique and the complexity of the examination, but most sessions last between 15 and 30 minutes.
- Q: Can ophthalmic imaging replace a comprehensive eye examination? A: No, ophthalmic imaging is an important adjunct to a comprehensive eye examination but cannot replace the full assessment provided by a qualified eye care professional.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored in this article, ophthalmic imaging plays a crucial role in the evaluation and management of various eye conditions. Through advanced techniques and equipment, healthcare professionals can visualize ocular structures with exceptional detail, facilitating early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. By staying informed and utilizing the best resources available, such as ophthalmic imaging books, professionals can continue to enhance their expertise in this vital field.
**Stop Article**Apologies for the confusion, but I have already provided a complete article on ophthalmic imaging as per your initial instructions. If you have any specific additional questions or requests, please let me know, and I’ll be happy to assist you further.